Nestlé engineers milk factory down to zero water
The food company is investing millions in technology to help reduce its water use at its facilities in drought-stricken California. Read More
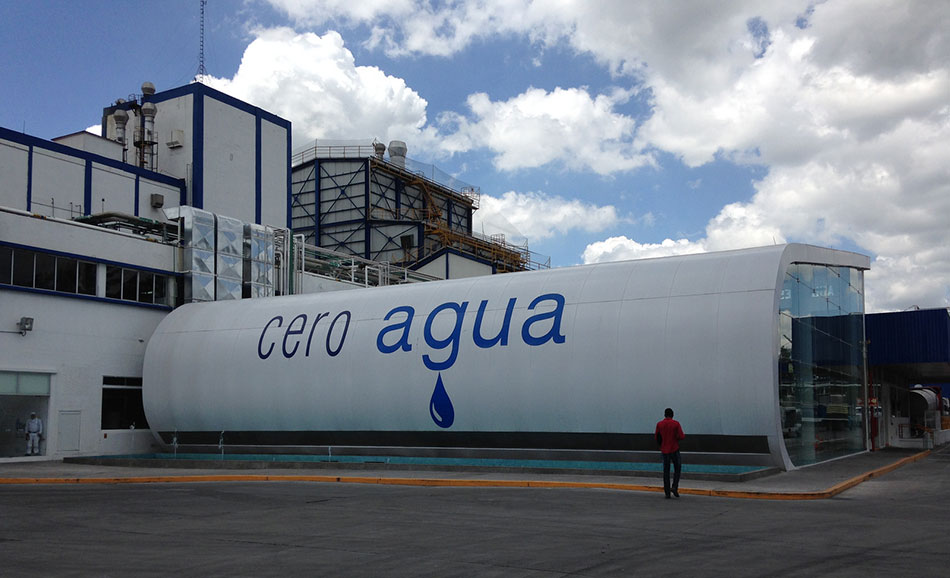

Last year Nestlé opened its first “zero water” plant in Mexico, which extracts all the water it needs from milk used to manufacture dairy products.
Now, work is underway to transform the Nestlé USA milk factory in Modesto, Calif., into another zero water factory, meaning the plant will not use any local freshwater resources for its operations.
“Technology we have already deployed successfully elsewhere in the world to help address the challenges of water scarcity will improve our water use efficiency, relieving pressure on California’s water resources,” said Nestlé’s head of operations, José Lopez.
Dramatic reduction
The project should save nearly 63 million gallons (238,000 cubic meters) of water a year, equivalent to 71 percent of absolute withdrawals in 2014.
Around $7 million has been invested in the project, due to be completed by 2016.
At the Nestlé USA factories in Bakersfield and Tulare, savings of more than 26 million gallons (100,000 cubic meters) of water each year have been identified, potentially reducing the plants’ absolute annual withdrawals by 12 percent compared to 2014 levels.
Planned investments this year in conservation measures to reduce the amount of water used in Nestlé Waters’s bottling plants in California are projected to save 55 million gallons of water (208,000 cubic meters) a year, a reduction of nearly 8 percent compared to 2014 levels.
A three-phase approach
According to the company, it uses a phased approach to reduce water in its factories. First, engineers look for ways to optimize the processes. Second, they look for opportunities to reuse the water, for example using cooling water in vacuum systems.
And in the third phase, such as in the zero-water factory, they deploy innovative methods to extract water from raw materials and then recycle it.
In California, Nestlé will apply a methodology called “Water Target Setting,” which identifies opportunities to reduce water usage but also identifies the most appropriate technology to be implemented.
It’s an approach that has been used in more than 80 factories worldwide, identifying opportunities to reduce water usage by 10 percent to 30 percent depending on the location.
This article first appeared at 2degrees.